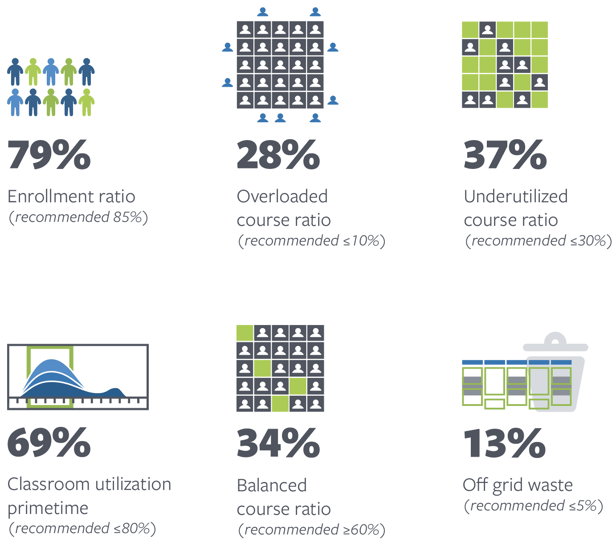
Definition: The percentage of unique courses offered that are balanced with student need, defined as having an enrollment ratio between 70% and 95%
Service: Strategic Scheduling

Increasing Enrollment Health Through Strategic Scheduling
Interstate transfer and capacity bottlenecks were an issue in Texas. After the passing of State Bill 25, Texas institutions implemented strategies to resolve these problems and become more efficient. Learn where the state of Texas began, adjustments made, and the impact of these scheduling changes.

In response to unclear academic course sequences in 2019, which resulted in students retaking courses they had already completed due to the lack of transfer, Texas passed State Bill 25. To mitigate this issue, this bill focuses on the facilitation of interstate transfer, academic progress, and timely graduation through the design and roll-out of recommended course sequences. Now, institutions are required to report non-transferable credits. In addition, this State Bill 25 requires universities to develop recommended course sequences for all their majors so that students can see the forest through the trees. This visibility helps students understand their commitment upfront and encourages completion.
By implementing strategies in response to Texas Senate Bill 25, Texas institutions began working with Ad Astra to identify capacity bottlenecks. This work revealed that general education courses required additional sections. In response, our Texas partners added new course sections to increase course capacity and improve degree velocity, adding availability to their course sequences. Ad Astra’s Higher Education Scheduling Index (HESI), a database for course scheduling that tracks 50 variables related to course scheduling patterns and institutional activity, found Texas partners improved critical areas in the course schedule that led to significant impacts on individual campuses.
Ad Astra partners with over 60 Texas higher education campuses, districts, and systems to ensure capacity and access to required courses. This work includes integrating institutional course scheduling and resource allocation with the recommended degree sequences that are rolled out through advising and registration. Positive results in degree velocity, early momentum, productive credit hours earned, and increased institutional capacity to meet demand are already showing as Ad Astra’s Texas partners continue to leverage their services and solutions to achieve state and institution goals.

When we began working with colleges and universities in Texas, we identified a few areas of improvement by analyzing some key metrics. If you're interested in learning more about these metrics, check out our key terms.
Definition: The percentage of unique courses offered that are balanced with student need, defined as having an enrollment ratio between 70% and 95%
Service: Strategic Scheduling
Definition: The percentage of hours in the primetime subset of a standard week (as defined by each institution’s usage patterns) that a typical classroom is in use
Software: Astra Schedule
Service: Strategic Scheduling, Meeting Pattern Analysis
Definition: The rate at which students complete their degree
Software: Predict, Align, Monitor
Service: Cohort Enrollment Health
Definition: The percentage of capacity wasted by scheduling non-standard meeting patterns during primetime hours
Software: Astra Schedule
Services: Strategic Scheduling, Meeting Pattern Analysis
Definition: The percentage of unique courses offered that are difficult for students to register for because they have a high enrollment ratio, defined as having an enrollment ratio of 95% or higher
Service: Strategic Scheduling, Pathway Analysis
Definition: The percentage of unique courses offered that are an inefficient use of faculty and classroom resources because they are under-enrolled, defined as having an enrollment ratio of less than 70%
Software: Predict, Align, Monitor
Service: Strategic Scheduling, Pathway Analysis

Midwestern State University focuses on two strategic goals: accelerating completion through alignment of the schedule to student need, and increasing schedule efficiency as well as proactively aligning course offerings. After implementing Ad Astra's change recommendations, course offerings in the fall 2019 schedule increased while the amount of overloaded, or bottlenecked, courses decreased. From Fall 2018 to Fall 2019, Midwestern State University experienced a five percent (5%) increase in their balanced course ratio and a three percent (3%) decrease in their overloaded course ratio, allowing positive results in degree velocity, early momentum, and productive credit hours earned. Pairing these student-centered scheduling strategies with other student support focused initiatives, Midwestern State University saw a year to year three percent (3%) increase in student retention.

University of Houston faced a difficult capacity challenge as the growing student population created fewer available classrooms. Through their work with Ad Astra, University of Houston uncovered specific opportunities that would yield additional classroom space in the short term, and highlighted schedule process changes that will help accommodate for projected growth through 2023. The opportunities concentrated on a more centralized scheduling process that balanced the need for department preferred scheduling and an optimized review by the University Registrar. This central review also created more consistent meeting patterns and less wasted space in critical primetime scheduling periods. Through the use of data modeling and targeted conversation, University of Houston leaders were able to roll out these recommendations in a shortened time span, opening classroom space for new sections and boosting the schedule to better meet student need.

Ad Astra is higher education’s solution partner in managing the academic enterprise. Partnering with more than 500 colleges, universities, and systems nationwide, Ad Astra helps improve stewardship of instructional resources, streamline student access to courses, and accelerate student completions.